Dielectric Constant Of Neoprene Rubber
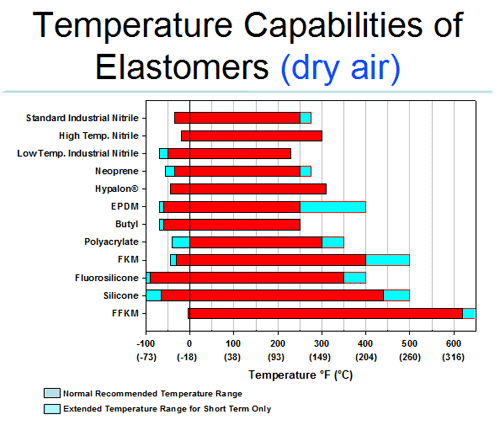
There are different types depending on functional groups in the structure and curing mechanisms.
Dielectric constant of neoprene rubber. This constant is defined as the capacitance of the material in question compared by ratio with the capacitance of a vacuum. Main applications are flexible seals o rings etc. Key properties include thermal stability chemical stability electrical insulation and low toxicity. Electrical and dielectric properties of rubber c.
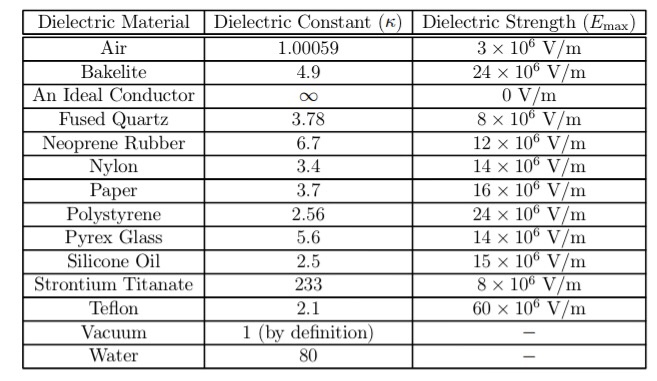
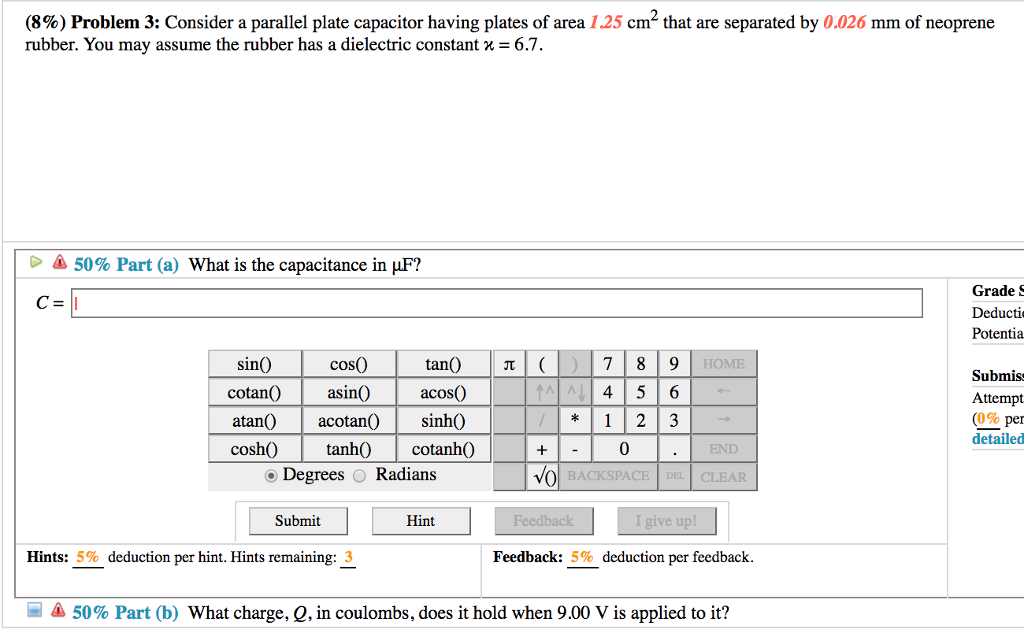
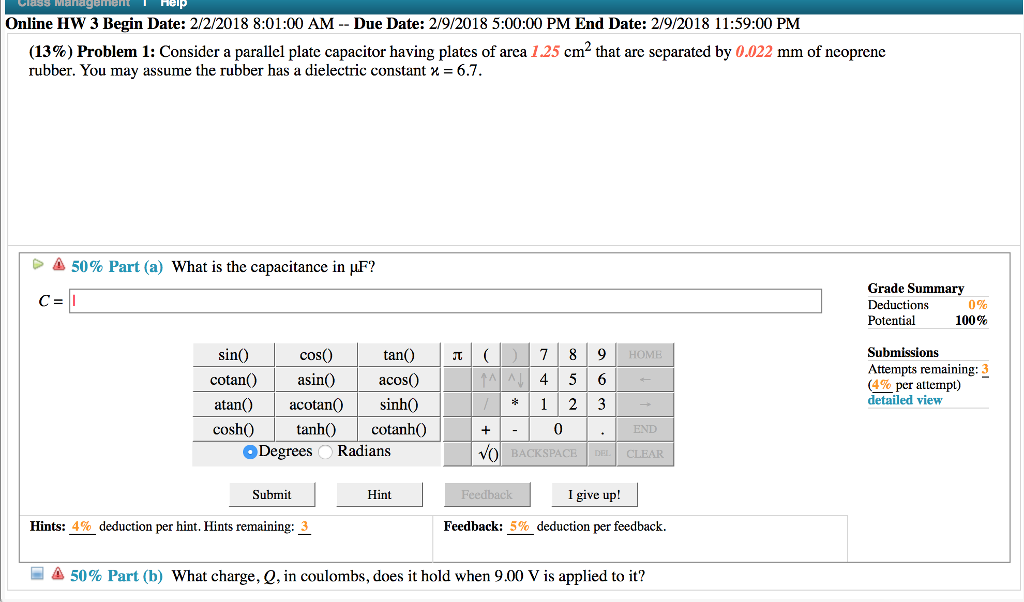
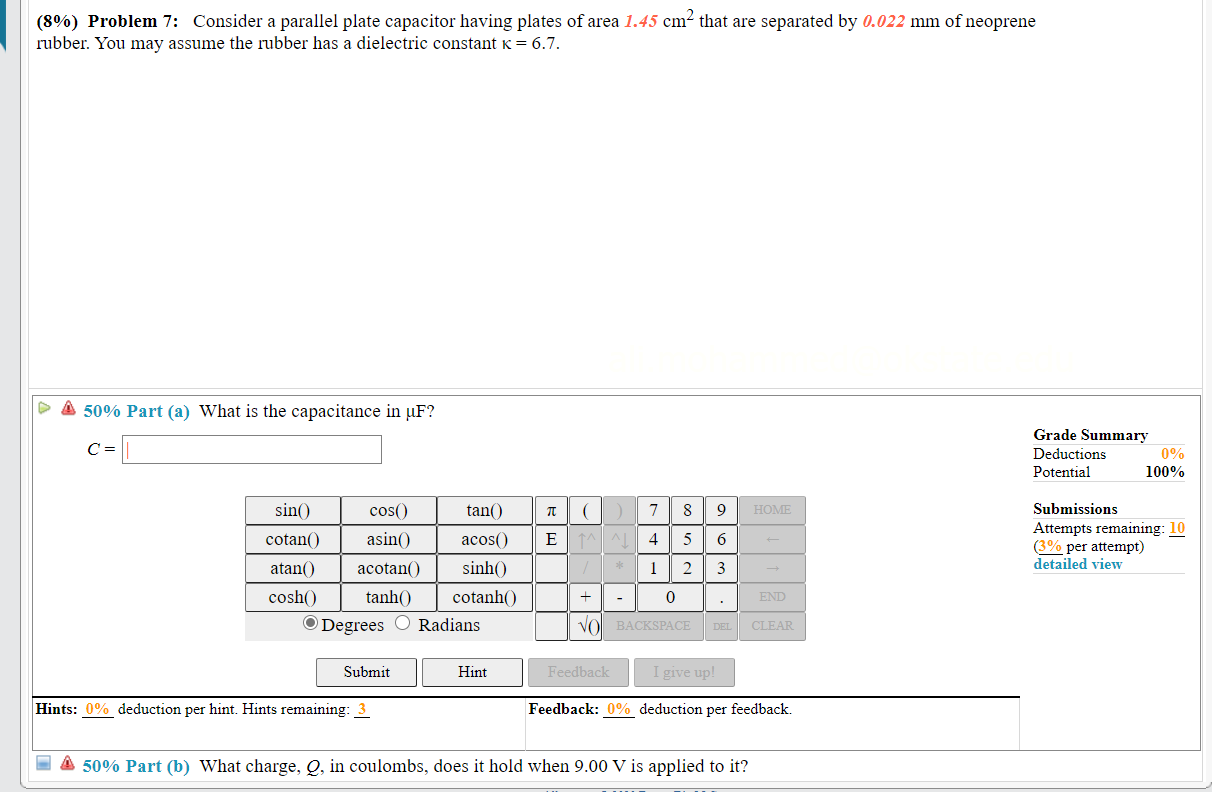
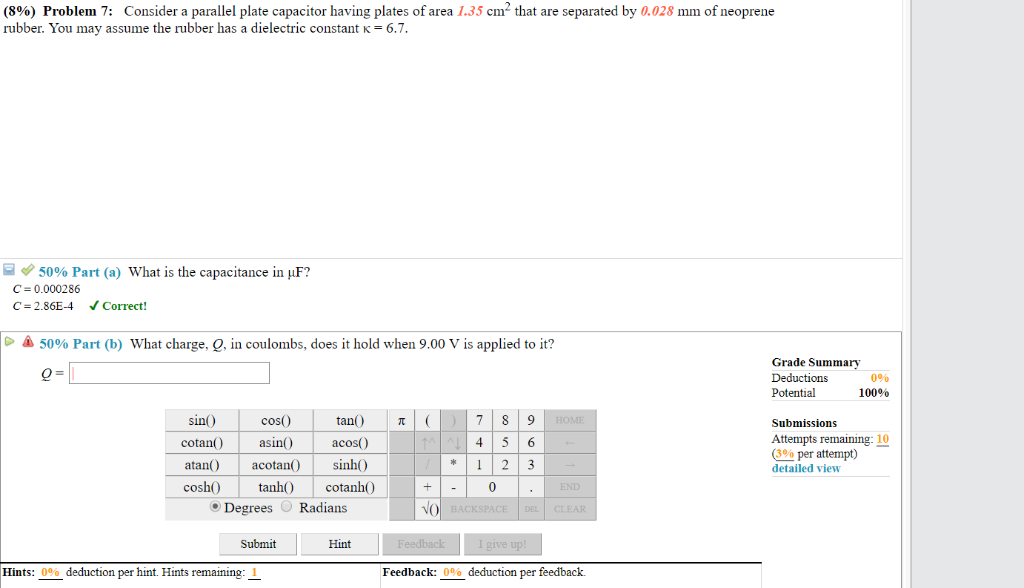
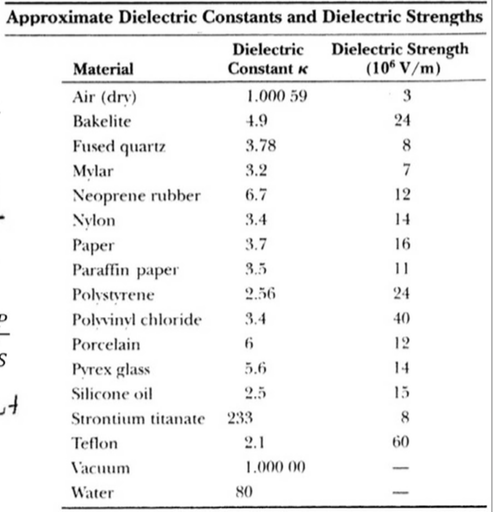
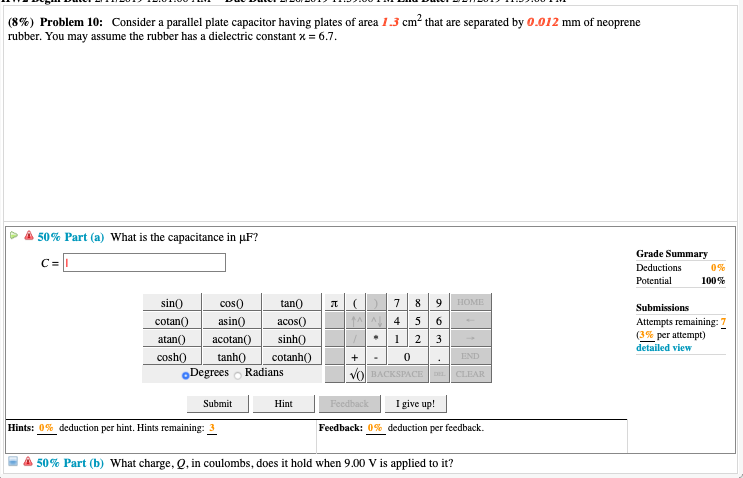
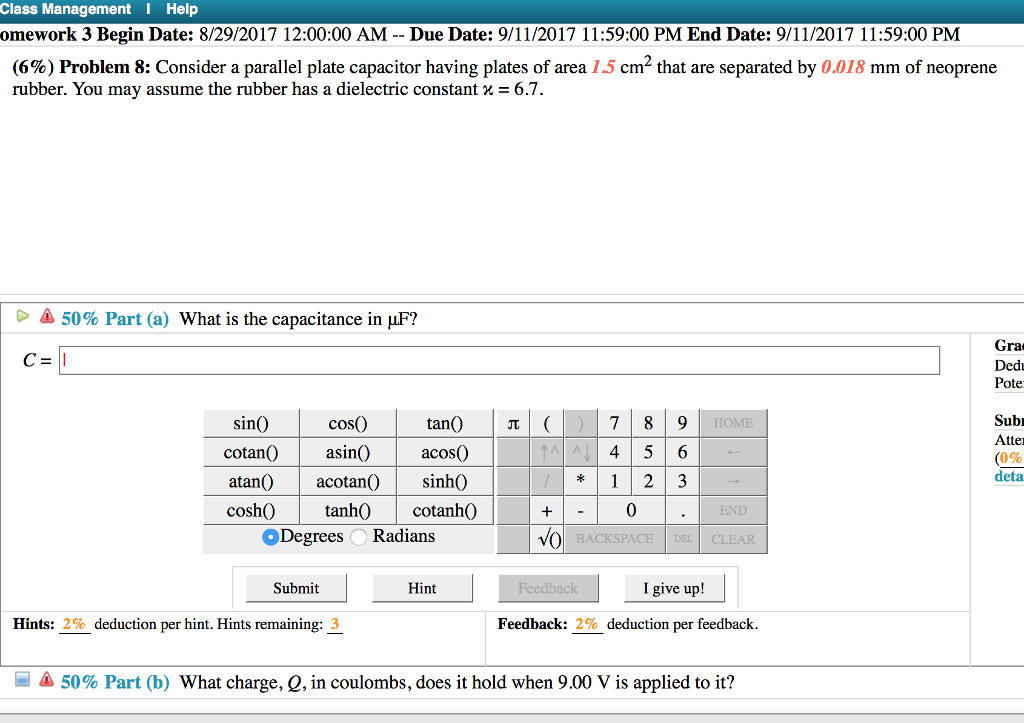
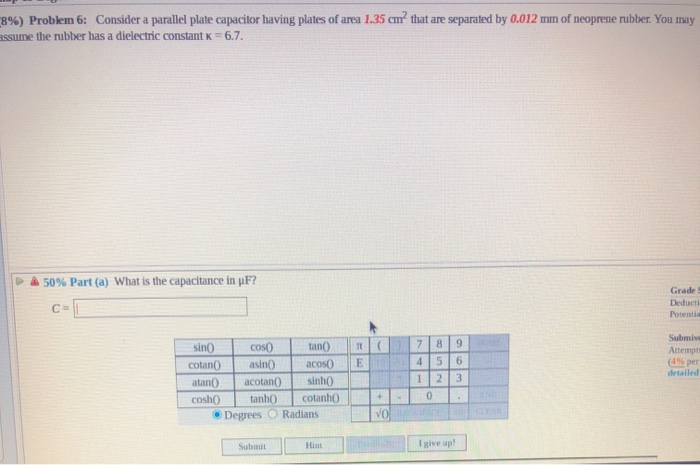
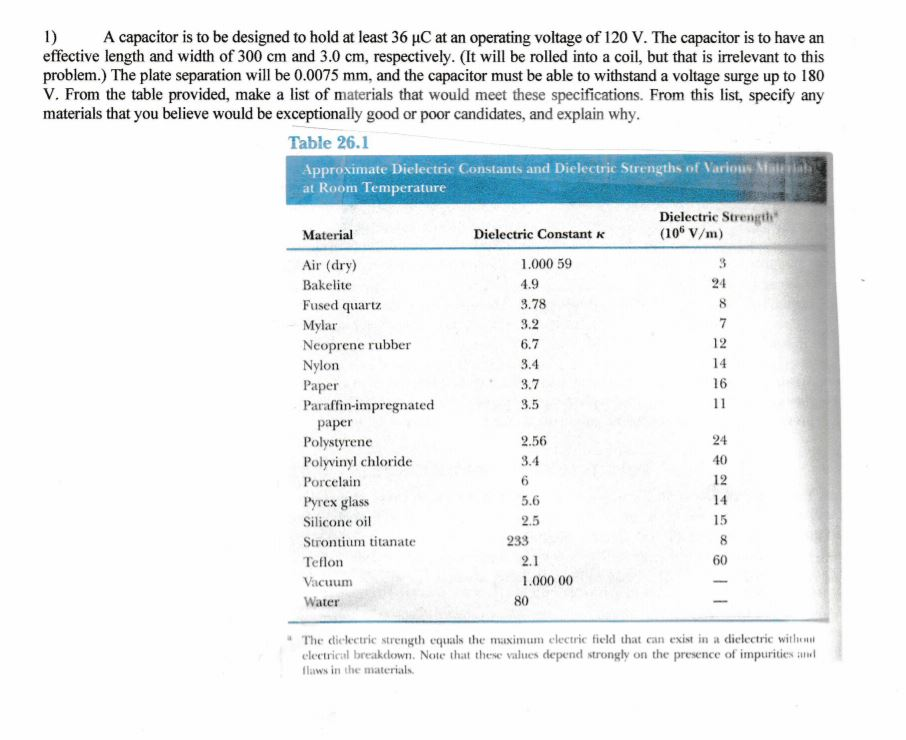
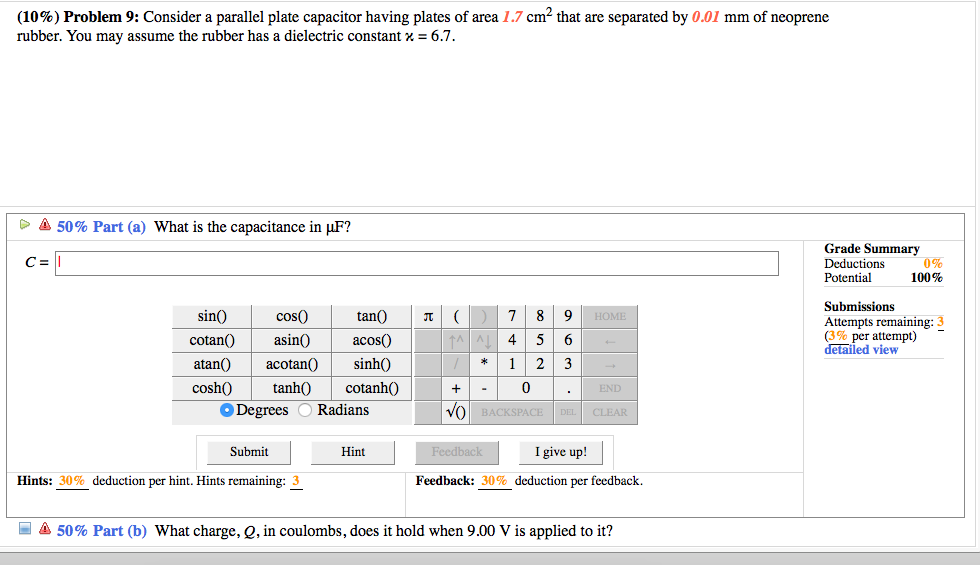
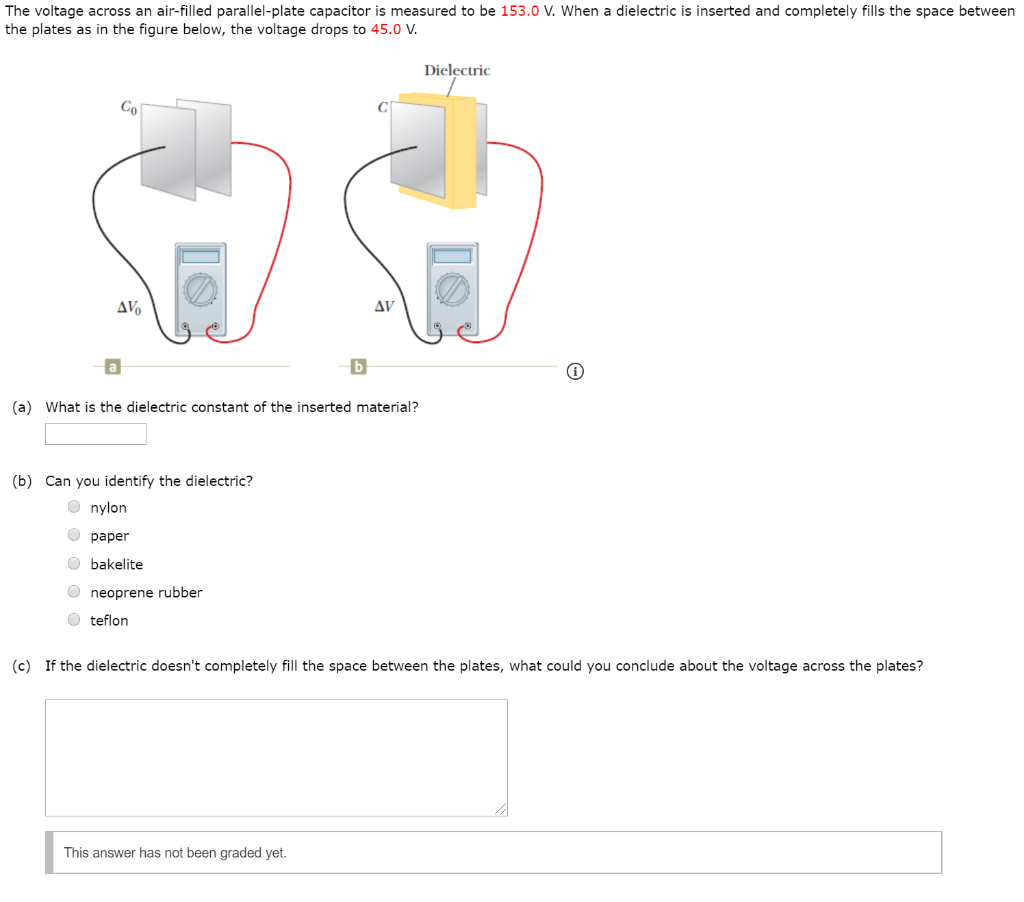
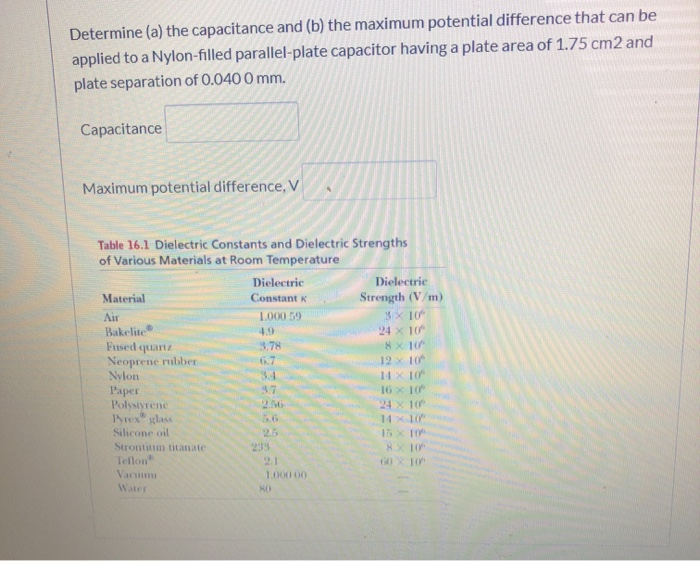
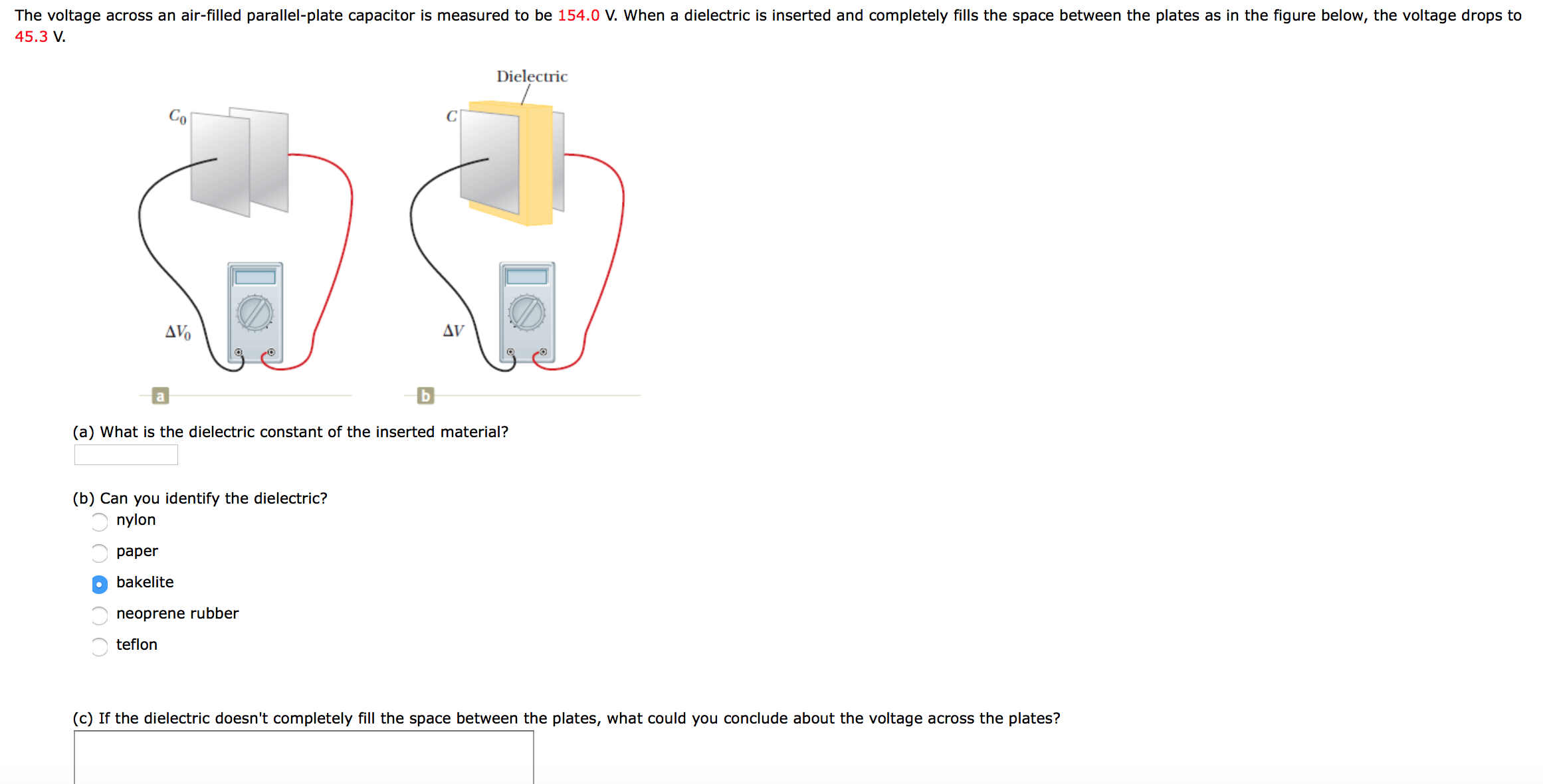
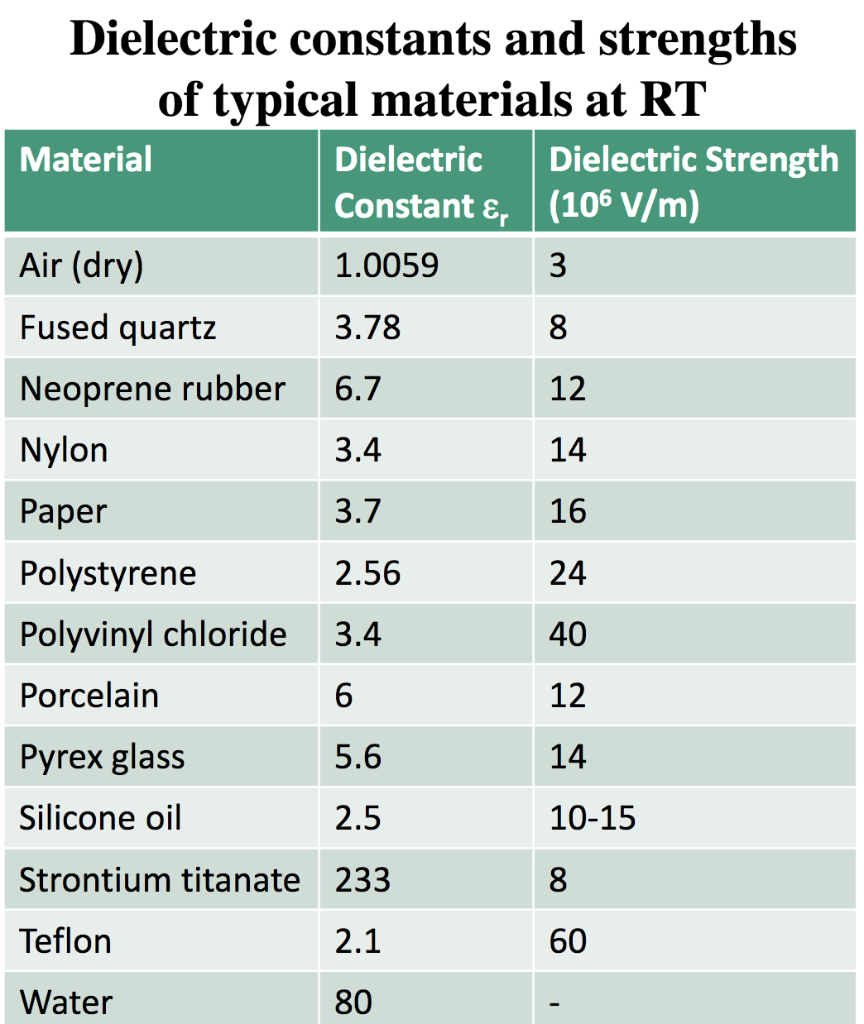
Dielectric constant k is a number relating the ability of a material to carry alternating current to the ability of vacuum to carry alternating current. In this case the dielectric material is neoprene rubber which has a dielectric constant of 6 7. The reinforcement makes it ideal for stress applications such as gaskets and diaphragm packings. Values of the dielectric constant κ for various materials are given in table 1.
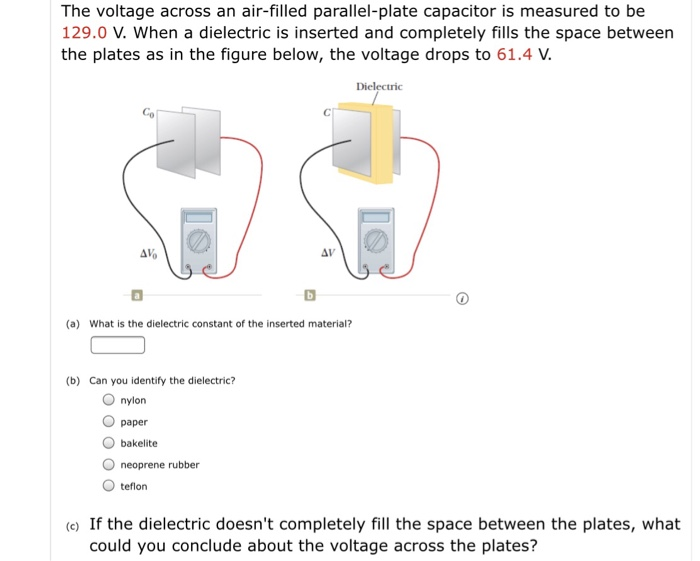
Dielectric constant or permittivity is a measure of how well the insulating material will act as a dielectric capacitor. As indicated by e r 1 00000 for a vacuum all values are relative to a vacuum. Note that κ for vacuum is exactly 1 and so the above equation is valid in that case too. If a dielectric is used perhaps by placing teflon between the plates of the capacitor in example 1 then the capacitance is greater by the factor κ which for teflon is 2 1.
Multiply by ε 0 8 8542 x 10 12 f m permittivity of free space to obtain absolute permittivity. Dielectric constants of various materials material min. Dielectric constant is a measure of the charge retention capacity of a medium. Fabric reinforced neoprene handles a good balance of oil flame and weather resistance.
The capacitance created by the presence of the material is directly related to the dielectric constant of the material. Roland naval research laboratory chemistry division code 6105 washington dc 20375 rubber chemistry and technology vol. Permittivity is a material property that affects the coulomb force between two point charges in the material. Values presented here are relative dielectric constants relative permittivities.
Silicones are polymers with a si o si backbone. 32 53 2016 abstract this review describes electrical and dielectric measurements of rubbery polymers. C 6 7 x 8 85 x 10 12 f m x 1 50 m 0 0200 x 10 3 m 4 45 µf the stored charge is. Air 1 1 amber 2 6 2 7 asbestos fiber 3 1 4 8 bakelite 5 22 barium titanate 100 1250 beeswax 2 4 2 8 cambric 4 4 carbon tetrachloride 2 17 2 17 celluloid 4 4 cellulose acetate 2 9 4 5 durite 4 7 5 1 ebonite 2 7 2 7 epoxy resin 3 4 3 7 ethyl alcohol 6 5 25 fiber 5 5.
Rubber sheeting cloth inserted neoprene. The relative permittivity or dielectric constant of a material is its absolute permittivity expressed as a ratio relative to the vacuum permittivity.